How to correctly calculate the fabric for curtains
Sometimes it happens that ready-made curtains presented in stores are not at all pleasing to the eye and categorically do not fit the interior of rooms in which it was urgently needed to buy new curtains. Then curtain fabric comes to the rescue, from which you can independently sew beautiful curtains that will definitely fit the design of a particular room.

To make good quality curtains with your own hands, you first need to choose the material, and then measure the room and determine how many meters of the selected material will be needed for a particular room. Only then can you start sewing.
How to choose fabric for curtains
When choosing a suitable fabric for making curtains, you need to rely on some of the main characteristics of the fabric:
- Practical to use. Here it is important to make sure that the fabric is easy to clean and that there will be no difficulty in cleaning it from dirt, hemming and other modifications.
- The durability of the canvas. The curtains in the rooms should be made of a fabric that does not wear out too quickly and does not deteriorate from sunlight (does not fade).
- The density of the fabric. If you need to make drapery, it is better not to take a thin fabric, it is worth taking a denser and heavier one.
- The ability to absorb moisture and odors. It is especially important in the kitchen - the aromas should not settle and eat into the canvas.
- Decorative function of the curtain. The fabric should be ideally combined with the design of the room and not draw too much attention to itself.

Also important is the place in which the curtains from a certain fabric will hang:
- In the living room: with low ceilings, it is better to give preference to such lightweight natural materials with a small addition of synthetics such as silk, linen or viscose. In a large room with high ceilings, choose a denser and heavier fabric like jacquard and brocade.
- In the bedroom: usually textiles are chosen for the bedroom, based on the needs of the residents and the design of the room - you can choose either a light, almost transparent fabric, or a dense version (for example, jacquard with silk inserts).
- In the nursery: for the rooms where children live, they usually choose curtains made from natural materials that can be washed in a washing machine or dry-cleaned - for a children's room it is better to buy cotton, linen or woolen curtains with impurities of artificial materials.
- In the kitchen: due to the constant concentration of various aromas and moisture in this room, it is worth choosing curtains made of artificial materials (for example, polyester), made like roman blinds or curtains.

Molton
What is Molton? Molton, also called molton or melton, is a fabric that looks like flannel but is very thick. It is a pleasant-to-the-touch fleecy fabric of natural origin, made from cotton and woolen fibers. Of the characteristics of the Molton, the following are worth noting:
- Naturalness of the composition.
- Absorbs moisture, but allows air to pass through.
- Maintaining the shape of the product.
- Molton is almost impossible to crush.
- Nice appearance of the fabric.
- High heat retention.
- Comfort.
- Durability and reliability.
- Density.
- Soundproofing effect.
- Easy to use and maintain.

Lanon
Lanon is a fabric as dense as molton, which has good thermal insulation and resistance to external factors among its characteristics. Lanon can be compared to natural wool, only it is more durable and made from artificial raw materials. This canvas can be classified as premium materials.
Usually lanon fabric can be found in three basic colors - white, beige or milky. This fabric is used for sewing the following items:
- Curtains.
- Curtains.
- Dresses.
- Costumes.
- Shirts.
- Jackets.
- Skirts.
- Pants.
- Coat.
- Bedspreads and blankets.
Things made of this material are heat-resistant, do not allow wind and moisture to pass through.
Boston
The Boston fabric (not to be confused with the name of a city in the USA) is a wool fabric made from merino yarn. Differs in naturalness, ease of care and durability. In the USSR, clothes made of Boston fabric were often made precisely because of the latter factor - things made from this material could be worn for decades and still not be demolished, the clothes remained in very good condition, practically like new.
There are several different types of boston:
- Slim, suitable for outerwear. Also suitable for suits and children's school uniforms.
- Medium, for making coats.
- Furniture option, for upholstery of sofas, armchairs.
- Boston for curtains. Quite dense fabric is usually embroidered with contrasting silk threads or has silk inserts.

Material pluses:
- Heat retention.
- Strength.
- Durability.
- Maintaining the shape of the product.

Cons of material:
- Damage by moths.
- Over time, the fabric begins to shine at the folds.
- May shrink after washing.
Cupro
Cupro fabric is similar to silk in many ways, but it is made from artificial raw materials. Typically, it is used to make clothes, upholstery, curtains or carpets. Often, cupro (there is also a variant of "cupra") is used for sewing lining or elegant garments.
Pros of kupor fabric:
- Breathability, lightness.
- The fineness of the fabric.
- The beauty of the material and products made from it (cupra shines and shimmers both in the sun and under electric light).
- Absorbs moisture.
- Strength.
- Wear resistance.
- Not influenced by external factors (does not fade).

Cons of fabric:
- The production of kuprovoy fabric is far from the concept of "environmentally friendly".
- The high cost of the canvas (due to the expensive production).

Moire
Moire fabric is a material that is interesting for its “creation of waves”, it creates shine and interesting patterns, and therefore it is best to sew elegant elements of clothing or curtains from this fabric into the “front” living room.
There are two types of moire fabric:
- Grimoire - characterized by the iridescence of a bright small pattern.
- Antique moiret - on the contrary, has a large print and overflows.
Advantages of fabric:
- Striking appearance.
- Good shape retention.
- Strength.

Cons of fabric:
- Difficulty leaving.
- If creases appear on the fabric from improper storage, most likely, the product is irrevocably damaged.

Net
Mesh is not just a material, it is a whole group of canvases, united by a special weaving of vertical and horizontal threads.

Mesh characteristics:
- Allows air to pass through.
- Dries quickly.
- Retains its shape.
- Durable.
- Easy to work with.
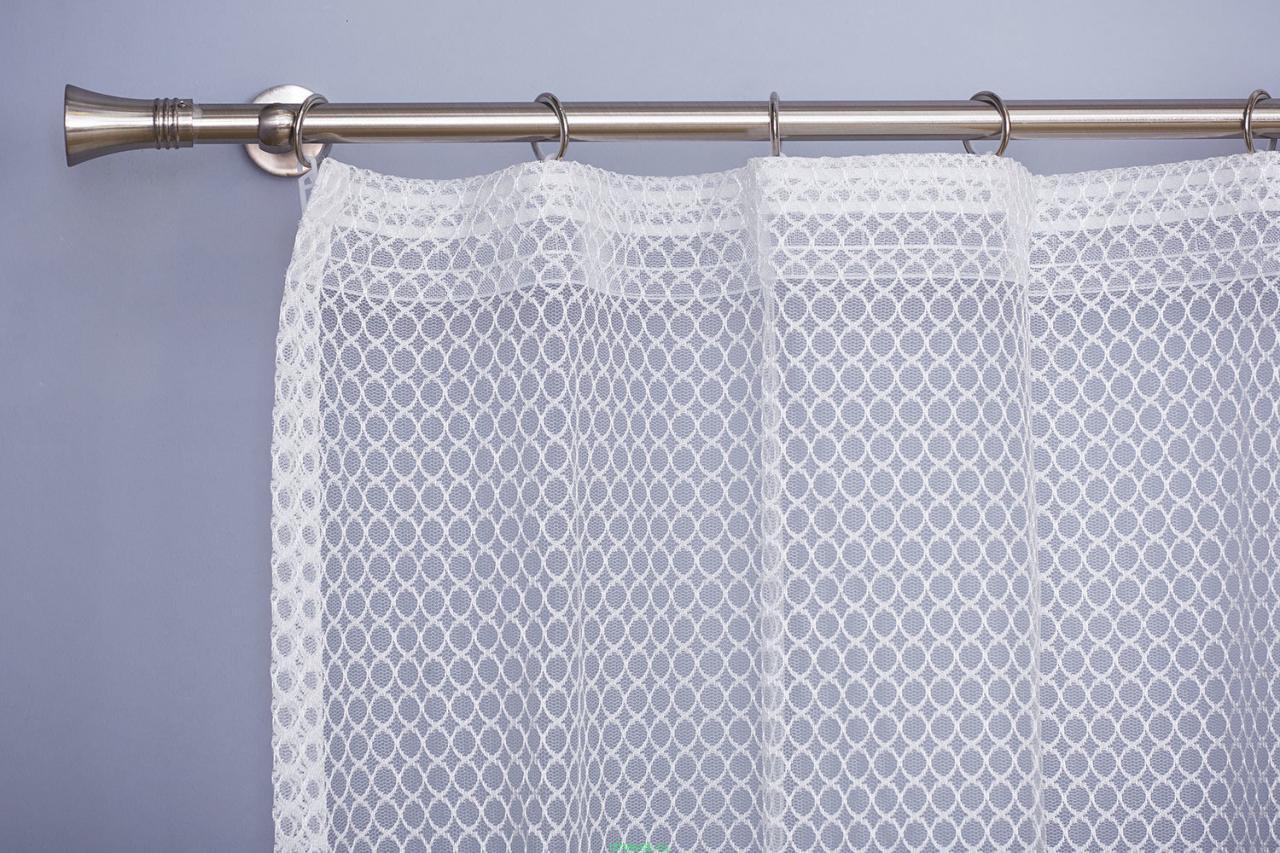

Cons of fabric:
- Moisture permeable.
- Transparent (cannot be used for sewing clothes without additional fabric).
- Tough, which is not very comfortable to wear.

Cotton
Cotton is a natural fabric that everyone has known since childhood. It is universal, you can sew almost anything from it.
Pros of cotton:
- Strength.
- Chemical resistance.
- Resistant to external factors (water and sunlight).
- Withstands high temperatures.
- Softness.
- Heat.
- Air permeability.

Cons of cotton:
- Tendency to deform.
- Can sit down.
- Wrinkles a lot.
- Dries slowly.

Linen
Linen is another fabric that absolutely everyone knows. It is made from natural materials and is used to make clothes and curtains.
Flax characteristics:
- Strength.
- Fast moisture absorption.
- It can withstand high temperatures (up to 170 degrees).
- Chemical resistance.
- Little stretching - not deformed.
- Inelastic.

Types of fabric:
- Twill.
- Patterned.
- Jacquard.
- Linen.
- Openwork.
How to calculate how much fabric you need
To calculate the fabric for the curtains, you can, of course, try to find video tutorials on the topic “how much fabric is needed for the curtains if the cornice is 3 meters, how to calculate how many meters of fabric is needed for the curtains and how to calculate the width of the curtains”. Or you can use the printed instructions. To count everything correctly, you need a tape measure, pencil or marker and paper for notes. You can draw a plan of the wall on which the cornice is attached in advance.

By lenght
To determine the length of the curtains, you must first decide how long they will be:
- To the windowsill. The bottom of the curtain is 1 centimeter higher than the surface.
- Below the windowsill. The bottom of the curtains hangs 10-15 centimeters below the surface of the windowsill.
- To the floor. The bottom of the curtain is 1 centimeter higher than the floor surface.
How to determine the length of the curtains, instructions:
- Measure the distance from the curtain rod to the level where the curtain should end.
- Take into account hem allowances.
By width
How to determine the width of the curtains, instructions:
The width of the curtain is calculated according to the type of fastening - it all depends on the assembly factor of the curtains. In addition, you need to add 10 centimeters to the sides so that later you can make side folds. The formula for calculating the width: eaves length * assembly factor (depending on the type of fastening.

Stock for curtains with large prints or pleats
What if you chose curtains with a pattern that repeats along the entire length of the canvas? In this case, it is necessary to increase the consumption by the length of the rapport of the main curtain pattern. You just need to add rapport to the formula for calculations.
Curtain assembly factor
The curtain assembly factor is needed to determine the width of the canvas, since it is by this factor that the length of the cornice will need to be multiplied. There are certain numbers associated with each individual type of attachment:
- Loops - 1.5-2.
- Eyelets - 2.
- Pencil folds - 2-2.5.
- Triple folds - 2-2.5.
- Puffs - 2.5.

Using this data, you can calculate the width of the shade.
Thus, you can calculate any fabric for curtains in every room in the house using the formulas and data provided in the article. The main thing is not to make a mistake in your actions and not to confuse the numbers.
Video: how to choose fabric for curtains




























































